
Irregular periods are one of the most common concerns women experience at different stages of life. While occasional changes in the menstrual cycle may not always be alarming, consistent irregularity can indicate underlying hormonal, lifestyle, or medical issues that require attention. A healthy menstrual cycle is a strong indicator of overall reproductive and hormonal well-being, and disruptions should never be ignored.
Many women feel confused or anxious when their periods arrive earlier than expected, are delayed for weeks, or vary significantly in flow and duration. These changes can affect daily life, emotional stability, fertility, and long-term health. Understanding what irregular periods mean, why they occur, and how they can be managed empowers women to take better control of their reproductive health.
This detailed guide explains everything you need to know about irregular periods, including their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatment options.
A regular menstrual cycle usually lasts between 21 and 35 days, with bleeding lasting around 3 to 7 days. When this pattern changes frequently, the cycle is considered irregular. Irregular periods may involve missed cycles, unusually heavy or light bleeding, spotting between periods, or cycles that occur too frequently or too far apart.
Some women experience irregular periods occasionally due to stress, illness, or travel. However, when irregularity becomes frequent or prolonged, it may indicate an imbalance in the body’s hormonal system. Hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, and luteinizing hormone work together to regulate the menstrual cycle, and even small disruptions can affect cycle regularity.
Understanding your body’s natural rhythm and noticing changes early allows for timely evaluation and care.
Regular periods are a key sign that the reproductive system is functioning properly. They indicate that ovulation is occurring regularly and that hormones are balanced. When cycles become irregular, it may affect fertility, emotional health, and overall physical well-being.
Consistent menstrual cycles also help doctors identify potential health conditions early. Irregular periods can sometimes be the first sign of hormonal disorders, metabolic issues, or gynecological conditions. Paying attention to menstrual health is not just about reproduction—it is an essential part of overall wellness.
Maintaining regular cycles supports hormonal balance, stable energy levels, healthy skin, and emotional well-being.
Irregular periods can result from a wide range of physical, hormonal, and lifestyle-related factors. Understanding these causes is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.
Hormonal imbalance is one of the most common reasons behind irregular periods. Hormones such as estrogen and progesterone regulate ovulation and the menstrual cycle. When their levels fluctuate, ovulation may not occur regularly, leading to unpredictable cycles.
Hormonal imbalances can result from stress, poor diet, lack of sleep, or underlying medical conditions. Even small disruptions can affect the body’s natural rhythm, making periods early, late, or completely absent.
PCOS is a common hormonal disorder affecting many women of reproductive age. It often causes irregular or missed periods due to irregular ovulation. Women with PCOS may also experience weight gain, acne, excessive facial or body hair, and difficulty conceiving.
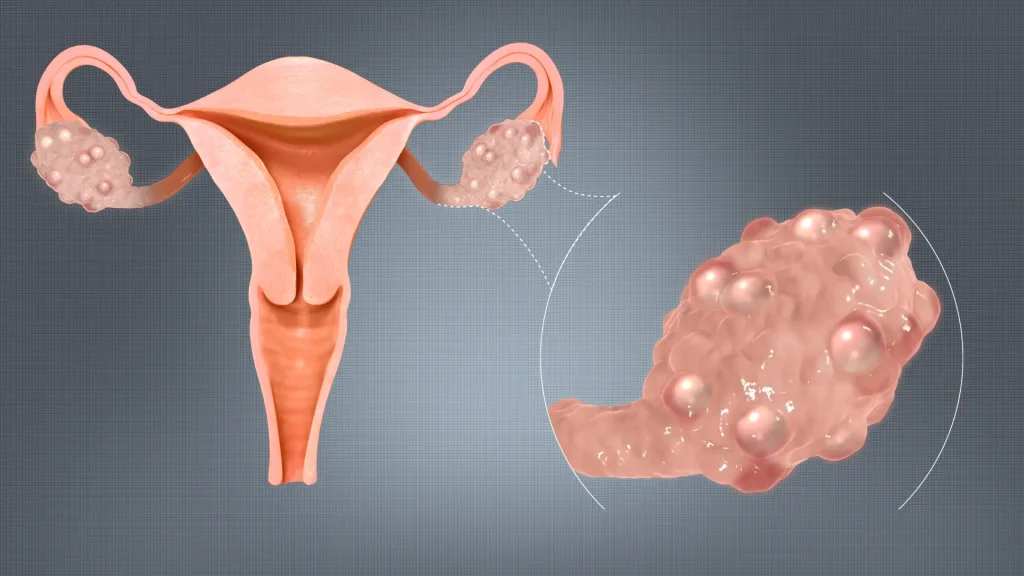
The condition is linked to insulin resistance and elevated androgen levels, which interfere with normal hormonal function. Without proper management, PCOS can lead to long-term health complications, including diabetes and infertility.
Stress plays a powerful role in menstrual health. When the body is under constant stress, it releases cortisol, which can interfere with the hormones responsible for ovulation. High stress levels may delay or completely stop ovulation, resulting in irregular periods.
Emotional stress, anxiety, and mental exhaustion can all disrupt the body’s natural rhythm. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, proper sleep, and emotional support is essential for hormonal balance.
Rapid weight loss or weight gain can significantly affect menstrual cycles. Extremely low body fat can prevent ovulation, while excess body fat can increase estrogen levels, leading to irregular bleeding.
Maintaining a healthy and stable weight supports hormonal regulation and promotes regular menstrual cycles.
The thyroid gland plays a critical role in regulating metabolism and hormone production. Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can disrupt menstrual cycles, causing irregular periods or changes in flow.
Symptoms may include fatigue, weight changes, hair thinning, and sensitivity to temperature. Treating thyroid disorders often helps restore normal menstrual patterns.
While exercise is beneficial, excessive physical activity can place stress on the body and interfere with hormone production. Athletes and individuals with intense workout routines may experience missed or irregular periods due to low energy availability.
Balancing exercise with adequate nutrition and rest is essential for maintaining menstrual health.
Hormonal contraceptives can cause temporary changes in menstrual patterns, especially during the first few months of use. Some women experience spotting, lighter periods, or skipped cycles.
Certain medications, including antidepressants and hormonal therapies, may also affect the menstrual cycle.
As women approach menopause, hormonal fluctuations become more frequent. Periods may become irregular, lighter, or heavier before eventually stopping altogether.
This transitional phase can last several years and is a natural part of aging.
Irregular periods may occur alongside other symptoms that provide insight into underlying health conditions. These symptoms can include:
Tracking these symptoms helps healthcare providers make accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans.
Medical attention is recommended if irregular periods:
Early diagnosis ensures timely treatment and prevents potential complications.
Diagnosing irregular periods involves a comprehensive evaluation that may include:
These tests help identify the root cause and guide effective treatment.
Treatment depends on the underlying cause, age, lifestyle, and reproductive goals.
Simple lifestyle adjustments often have a significant impact. These include maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress, exercising moderately, and ensuring adequate sleep.
Healthy habits help restore hormonal balance naturally.
Hormonal treatments may be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles and manage hormonal imbalances. These therapies help stabilize estrogen and progesterone levels.
If an underlying medical condition is identified, targeted treatment is essential. Treating thyroid disorders, PCOS, or infections often restores normal menstrual patterns.
For women trying to conceive, fertility-focused treatments may help regulate ovulation and improve reproductive outcomes.
Irregular periods can take an emotional toll, causing anxiety, frustration, and stress. The uncertainty of unpredictable cycles often affects confidence and mental well-being.
Seeking emotional support and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers can significantly improve quality of life.
Although not all causes are preventable, certain steps can help reduce the risk:
Prevention and early intervention play a key role in long-term health.
With proper care and guidance, most women can successfully manage irregular periods. Understanding your body, maintaining healthy habits, and seeking professional support empower you to take control of your reproductive health.
Consistency, awareness, and timely care make a significant difference in long-term well-being.
Irregular periods are a common but important health concern that should not be ignored. While occasional changes may be normal, persistent irregularity often signals an underlying issue that requires attention.
By understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms, and seeking appropriate treatment, women can regain balance, confidence, and control over their menstrual health. If irregular periods are affecting your quality of life, consulting a healthcare professional is the first step toward clarity and healing.
Women Health By Dr. Namrata Jadhav 2025 | All Rights Reserved.
Need help? Chat with us