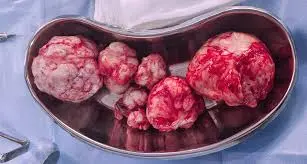
Uterine fibroids are one of the most common gynecological conditions affecting women, particularly during their reproductive years. Despite their prevalence, many women are unaware they have fibroids until symptoms begin to interfere with daily life or a routine gynecological checkup reveals their presence. For some, fibroids remain silent and harmless, while for others, they may cause significant discomfort, menstrual changes, or fertility concerns.
Fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus. Although they are benign, their impact on a woman’s physical comfort, emotional well-being, and reproductive health can be substantial. Understanding uterine fibroids helps women recognize symptoms early, seek timely medical care, and make informed decisions about treatment.
This blog is designed to educate women about uterine fibroids in a clear and reassuring way, while also explaining how expert gynecological care plays a crucial role in managing this condition effectively.
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas or myomas, are benign tumors that arise from the muscle tissue of the uterus. They vary in size, shape, and number, ranging from very small growths that go unnoticed to larger masses that distort the uterus.
Fibroids can grow within the uterine wall, project into the uterine cavity, or extend outward from the uterus. Their location often determines the type of symptoms a woman experiences. Importantly, uterine fibroids are not cancerous and do not increase the risk of uterine cancer.
Many women live with fibroids for years without symptoms, while others experience noticeable changes that prompt medical evaluation.
Uterine fibroids are extremely common, especially among women between the ages of 30 and 50. Studies suggest that a significant percentage of women will develop fibroids at some point in their lives, although not all will require treatment.
Hormonal activity plays a major role in fibroid development, which is why they tend to grow during reproductive years and often shrink after menopause. Genetic factors and lifestyle elements may also influence who develops fibroids and how they progress.
Understanding their prevalence helps normalize the condition and encourages women to seek information rather than silently managing symptoms.
Fibroids are classified based on their location within or around the uterus. Each type may present differently and affect menstrual and reproductive health in distinct ways.
Intramural fibroids develop within the muscular wall of the uterus. They are the most common type and may cause enlargement of the uterus, heavy menstrual bleeding, and pelvic pressure as they grow.
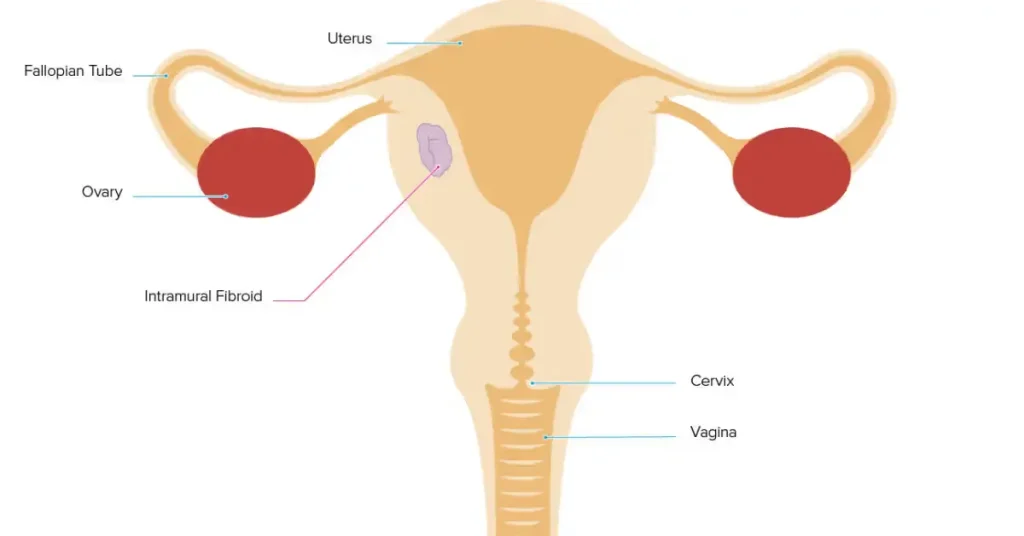
When intramural fibroids become large, they can affect surrounding organs and contribute to discomfort or pain.
Submucosal fibroids grow just beneath the uterine lining and may extend into the uterine cavity. These fibroids are often associated with heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding and fertility challenges.
Even small submucosal fibroids can cause significant symptoms because of their location.
Subserosal fibroids grow on the outer surface of the uterus. They are more likely to cause pressure-related symptoms such as pelvic discomfort, frequent urination, or lower back pain rather than heavy bleeding.
Pedunculated fibroids are attached to the uterus by a stalk. Depending on their position, they may cause sharp pain or discomfort, especially if the stalk twists.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids vary widely. Some women experience multiple symptoms, while others may have none at all.
One of the most common symptoms of uterine fibroids is heavy menstrual bleeding. Women may notice longer periods, increased flow, or the need to change sanitary products frequently.
Chronic heavy bleeding can lead to iron deficiency anemia, causing fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
Fibroids can cause a sensation of heaviness or pressure in the lower abdomen or pelvis. Larger fibroids may press on nearby organs, leading to discomfort or pain that worsens over time.
Pelvic pressure may also affect posture and daily movement.
When fibroids press against the bladder or bowel, they can cause frequent urination, difficulty emptying the bladder, constipation, or bloating.
These symptoms are often mistaken for urinary or digestive issues, delaying accurate diagnosis.
Some women with uterine fibroids experience pain or discomfort during intimacy. This may be related to fibroid location or uterine enlargement.
Addressing this symptom is important for both physical comfort and emotional well-being.
While many women with fibroids conceive naturally, certain fibroids can interfere with fertility or pregnancy. Submucosal fibroids, in particular, may affect implantation or increase miscarriage risk.
Proper evaluation helps determine whether fibroids are contributing to fertility challenges.
The exact cause of uterine fibroids is not fully understood, but several factors are known to contribute to their development.
Hormones such as estrogen and progesterone stimulate fibroid growth, which explains why fibroids are more common during reproductive years. Genetics also play a role, as fibroids tend to run in families.
Other contributing factors may include early onset of menstruation, obesity, and lifestyle influences. Fibroid development is usually the result of multiple interacting factors rather than a single cause.
Diagnosis often begins with a detailed discussion of symptoms and a pelvic examination. Many fibroids are detected during routine gynecological checkups, even before symptoms develop.
Ultrasound imaging is commonly used to confirm the presence, size, and location of fibroids. In some cases, additional imaging such as MRI may be recommended for more detailed evaluation.
Accurate diagnosis is essential for choosing the most appropriate management approach.
Treatment for uterine fibroids depends on symptom severity, fibroid size and location, age, and reproductive plans. Not all fibroids require treatment, and management is often individualized.
For women with small fibroids and minimal symptoms, careful monitoring may be recommended. Regular follow-ups allow the gynecologist to track fibroid growth and address symptoms if they develop.
This approach avoids unnecessary intervention while ensuring patient safety.
Medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms such as heavy bleeding or pelvic pain. Hormonal therapies can help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce symptom severity.
Medical treatment does not eliminate fibroids but can significantly improve quality of life.
In some cases, minimally invasive procedures may be recommended to target fibroids while preserving the uterus. These options depend on fibroid characteristics and patient goals.
A gynecologist helps determine whether such treatments are appropriate based on individual needs.
Surgery may be considered for large fibroids, severe symptoms, or fertility-related concerns. The type of surgery depends on whether future pregnancy is desired.
Surgical decisions are made carefully, with a strong emphasis on patient education and informed consent.
Dr. Namrata Jadhav brings a thoughtful, patient-centered approach to managing uterine fibroids. She focuses on understanding how fibroids affect each woman’s daily life, reproductive plans, and long-term health rather than treating imaging findings alone.
Her expertise lies in accurate diagnosis, individualized treatment planning, and clear patient education. Dr. Namrata emphasizes conservative management whenever possible while ensuring timely intervention when symptoms impact quality of life or fertility.
Women appreciate her balanced approach, which combines medical knowledge with compassionate care and open communication.
Many women live full, healthy lives with uterine fibroids. With proper monitoring, lifestyle adjustments, and medical guidance, symptoms can often be managed effectively.
Maintaining regular gynecological checkups and staying informed about bodily changes play a key role in long-term wellness.
Medical consultation is recommended if fibroid symptoms worsen, periods become excessively heavy, pain interferes with daily activities, or fertility concerns arise.
Early evaluation allows for more treatment options and better outcomes.
Uterine fibroids are common, manageable, and often misunderstood. While they are non-cancerous, their impact on menstrual health, comfort, and fertility can be significant if left unaddressed.
By understanding symptoms, seeking timely diagnosis, and working with an experienced gynecologist, women can make confident decisions about their care. Expert guidance from specialists like Dr. Namrata Jadhav ensures that uterine fibroids are managed with precision, compassion, and a focus on long-term well-being.
Women Health By Dr. Namrata Jadhav 2025 | All Rights Reserved.
Need help? Chat with us